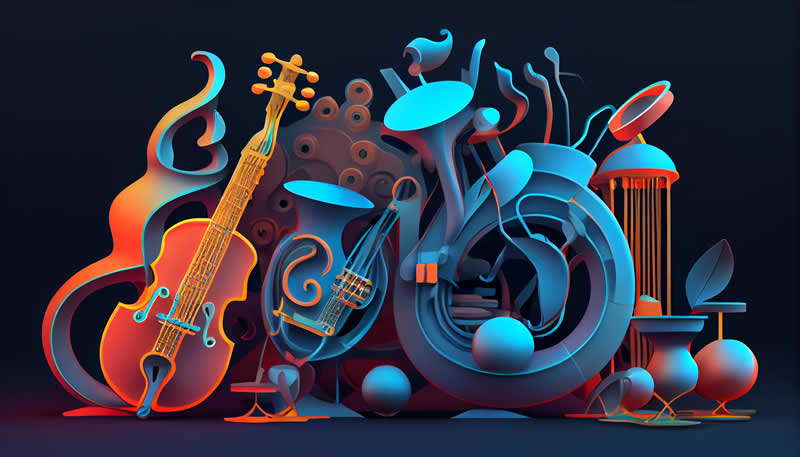
The 9 best Jazz instruments
Are you curious about the most popular jazz instruments? Or perhaps you're attempting to jazz up your music?
Jazz music's evolution has a very fascinating past. This genre of music is a result of the yearning for self-expression mixed with traditional African sounds.
Everyone deserves to have a voice, and because African-Americans were and occasionally still are subjected to severe oppression, thoughts were suppressed.
Music provided additional channels for the vocalization of ideas. A few very different instruments were used to artistically combine the traditional sounds imported from the African continent, and the name "jazz" was created to characterize the result.
The most popular jazz instruments are shown in the following images and explanations, enjoy!
Trumpet
Invention of trumpets dates around 1500 BC. The device served as a combat trumpet during that time. It later evolved into a musical instrument in the 14th and 15th centuries.
The lovely trumpet is the jazz band's highest-pitched instrument. When performed by a skilled performer, the tonal quality is extremely crisp and clear. A jazz band can portray a composition with either a very quick speed or with sluggish, drawn-out sounds.
The trumpet is made of brass and produces its tone by buzzing the lips inside of its mouthpiece. By altering the lips' form and fingering its three valves, sounds may be adjusted. From early jazz to modern genres, the trumpet has been a crucial component of the jazz ensemble thanks to its magnificent tone.
The trumpet is arguably the instrument most closely linked with jazz, in part because Louis Armstrong, a jazz legend, played it.
Drum set
Jazz music first used these incredible drums in the early 1900s, and their main function was to keep time. The music's tone or mood might also be changed by using the drums.
Jazz drum sets often only include a few components, despite the fact that they can comprise a wide variety of percussion instruments.
- A pedal is used to play the bass drum, which is the lowest drum.
- The hi-hat is a pair of miniature cymbals that crash together and are also played with a pedal. They serve as sharp accents.
- Sticks are used to play the snare drum.
- A crash cymbal, which is intended to highlight intense times.
- A ride cymbal, which is played continuously to provide color to the overall sound.
In contrast to other types of music, drums are performed differently in jazz. In addition to keeping the beat, drummers had to be flexible. According to legend, one of the first drummers to master the drums in this brand-new genre was Sid Catlett.
Guitar
The guitar is the most frequently utilized instrument in all musical genres and is particularly well-liked in jazz. Guitars make it possible for musicians to play hundreds, if not thousands, of different notes, making them one of the most adaptable tools in the whole world.
For its clarity, jumbo or hollow-body guitars are employed in jazz. Electric guitars are more frequently used by jazz artists to play either solos or rhythm.
Clarinet
The clarinet has been a component of jazz from its origin, just as the trumpet and piano are. This instrument was widely used in swing and New Orleans jazz in the 1930s and 1940s.
It is thought that Johann Christoph Denner invented the clarinet. It was created in Germany in the 1700s, and later technical advancements were made to it to increase the intonation and usability.
Jazz nowadays does not include the clarinet as often, but when it does, its warm, round tone draws special attention. The tone of the clarinet, a member of the woodwind family, is created when the reed on the mouthpiece vibrates.
Sydney Bechet, the first jazz soloist, and Johnny Dodds, who began playing the clarinet at age 17 and was trained by Louis Armstrong and Joe "the King" Oliver, are two of the most well-known clarinet players.
Piano
One of the jazz rhythm section's most adaptable instruments is the piano. It can virtually produce the sound of a complete band by itself because of the range and variety of its abilities, and this is the reason why it’s one of the most important jazz instruments.
This instrument's 88 keys provide for a wide range of harmonic possibilities and the ability to play both extremely low and very high notes. The piano may be used as a percussive instrument, or it can be played softly and melodically.
Saxophone
One of the most dynamic jazz instruments is the saxophone. Since essentially the very beginning of jazz, the saxophone has been a major jazz instruments due to its adaptable, voice-like tone.
The saxophone is a woodwind instrument, although it is composed of brass. By blowing into the mouthpiece, a cane reed vibrates to produce the instrument's tone.
The saxophone can only play one note at a time since it is a monophonic instrument. This indicates that its function is often to solo as well as play the melody, or "the head," of a song.
Famous saxophonists include Coleman Hawkins and Lester Young, known as "The Fathers of Jazz Saxophone," who created the jazz music's softer, smoother tones.
Trombone
Brass is used to make trombones. It makes use of a movable pipe that enters and exits the instrument's front end. Different notes may be produced by moving the slide pipe around.
Tenor trombones are typically used as jazz instruments because they produce the liveliest sound and are the most practical for performing the wide ranges frequently employed in jazz music.
Early on in the jazz era, trombones were utilized mostly as a background instrument, but during the swing era of jazz in the 1930s, they took center stage as a solo instrument.
Banjo
One of the first jazz instruments utilized to define jazz music was the banjo. The banjo was needed to maintain the rhythm of a piece, just like the drum was needed to maintain the beat. The guitar was occasionally substituted for the banjo later in the 1930s and into the 1940s.
Double Bass
Some of the slower tempo notes that are generally associated with jazz music are produced by the mellow double bass. This instrument may be played quickly with a thump-thumping motion to produce an upbeat melody or traditionally slowly to produce a gloomy and bluesy jazz piece.
In jazz bands, the double bass instrument first appeared in the 1890s. Ray Brown, who was married to Ella Fitzgerald, and Charles Mingus are two well-known bassists.
Best Jazz instruments - Conclusion
Experimenting with musical instruments is not prohibited. Therefore, even if you lack the jazz instruments mentioned in this article, you may always try to experiment with other musical styles with the instruments you do have.
Please visit our blog area to read more posts about the music world if you enjoyed this one.
You're here because you love music, so please try to listen to it while video chatting with other people in CalypsoRoom.
In CalypsoRoom we believe music is the most powerful tool to bring people together, and that’s why we created a music social network online where you can meet friends or new people starting from the same song and listening to the music simultaneously connected by webcam.
Are you a music artist or label and do you want to give your music a further dimension? Do you own or co-own the master and publishing rights to your music? Consider to post it on CalypsoRoom listening to it together with your super fans, at the same time, connected by webcams.
Thanks for reading,
CalypsoRoom Team
back
Written by CalypsoRoom Editorial Team
The CalypsoRoom Editorial Team is a skilled and diverse group of writers, researchers, and industry specialists who have access to Calypso's data and information in order to give you broad knowledge about the music industry as well as helpful advice to help you manage your music and dancing career.
Updated January 2023
Company number: 681223
James's Walk 31, Dublin, Ireland
contact@calypsoroom.com
+353 (89) 435 8928